As connectivity becomes more important for real-time data collection and remote management, cellular monitoring systems have emerged as key solutions for a wide range of industries. These systems leverage mobile networks to enable efficient surveillance, asset tracking, healthcare monitoring, and environmental observation. Their flexibility eliminates the need for wired infrastructure, which is essential for improving security measures and increasing operational visibility in constantly changing environments. As a result, businesses and organizations can respond to evolving challenges more quickly and with greater insight.
Adopting cellular monitoring is not just about monitoring itself. It is part of a larger shift toward data-driven decision-making and proactive management. By leveraging mobile technology to quickly transmit data from sensors and devices, organizations position themselves to address risks, streamline workflows, and improve outcomes in real time. Understanding how these systems operate and their wide-ranging applications can be critical for those looking to enhance security, automate processes, or monitor assets remotely.
Table of Contents
Definition Of Cellular Monitoring Systems
A cellular monitoring system is a remote surveillance and data-collection framework that leverages cellular networks to transmit data between devices and centralized monitoring hubs. Instead of traditional wired setups, these systems operate wirelessly, making them exceptionally suitable for expansive, mobile, or isolated locations. This technology forms the backbone of modern smart monitoring and is used extensively in everything from security installations to environmental science initiatives.
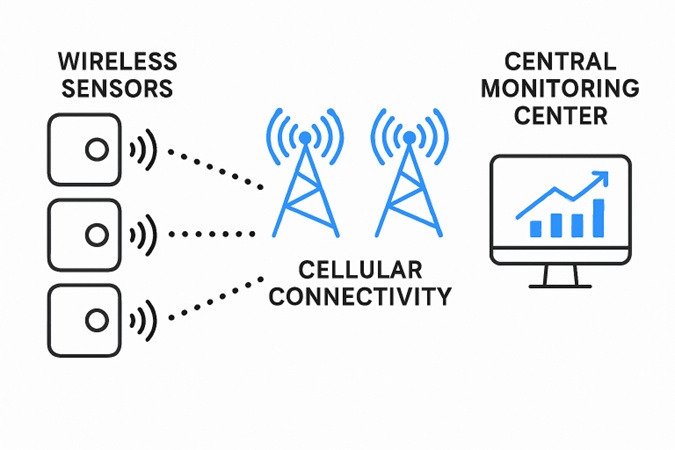
Key Components Of Cellular Monitoring Systems
Successful implementation of a cellular monitoring setup requires three crucial components:
- Sensors: These instruments detect and continually monitor variables such as temperature, movement, or air quality. Advanced sensors are often equipped with microprocessors for local data processing and anomaly detection before communication.
- Cellular Communicators: These modules use SIM cards and mobile communication protocols (such as 4G LTE or 5G) to send the data collected from sensors to the monitoring center.
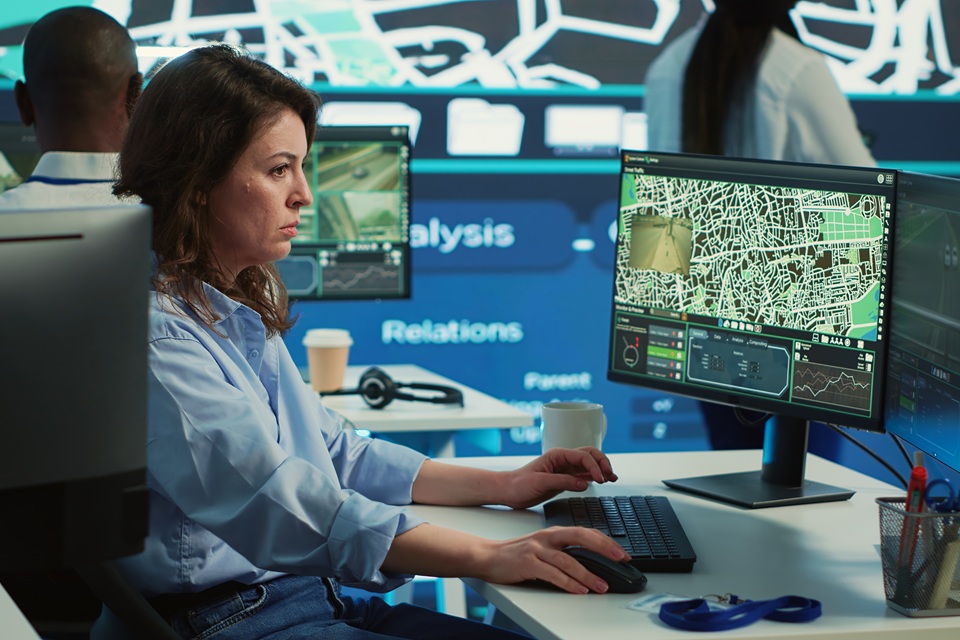
- Monitoring Centers: Central hubs that receive, aggregate, and analyze incoming data. Operators and intelligent software at these centers act on the information, whether that means dispatching security or notifying healthcare professionals.
How Cellular Monitoring Systems Operate
Cellular monitoring systems follow a logical sequence to ensure real-time response and continuous oversight:
- Data Collection: Sensors or devices continuously gather information about the chosen parameter or asset.
- Data Transmission: As soon as data is recorded or an alarm is triggered, the information is relayed via cellular communicators over mobile networks. This happens regardless of the device’s physical location, as long as cellular service is available.
- Data Analysis: The monitoring center receives the transmission, analyzes it using algorithms or manual operators, and takes action when required. This might involve sounding alerts, sending notifications, or activating safety mechanisms.
Integrating artificial intelligence into these processes is advancing rapidly, leading to smarter event detection and fewer false alarms.
Applications Across Different Industries
Cellular monitoring is not limited to any one sector. Some prominent applications include:
- Security and Surveillance: Building security solutions, outdoor monitoring, or fleet management systems deploy cellular cameras and sensors to relay instantaneous event footage and alerts.
- Healthcare: Remote health-monitoring devices send critical patient data to care teams via cellular networks. This is invaluable for managing chronic illnesses or supporting at-home care programs.
- Environmental Monitoring: Scientists and governments deploy networks of wireless sensors in remote or hazardous locations to monitor air quality, weather, or wildlife without needing physical infrastructure.
Benefits Of Implementing Cellular Monitoring Systems
There are several compelling reasons organizations opt for cellular-based monitoring:
- Flexibility: These systems can be installed and reconfigured quickly in places where wiring is impractical or impossible, such as temporary event sites or construction zones.
- Scalability: Adding new sensors or expanding coverage only requires deploying more wireless devices, without the cost or effort of rewiring existing infrastructure.
- Real-Time Data: Live access to data and alerts enables more agile, informed responses to incidents or operational changes, improving safety and efficiency.
Challenges & Considerations
Despite their advantages, cellular monitoring systems come with their own set of challenges:
- Network Coverage: These systems rely on cellular service. In remote, rural, or underground areas, spotty coverage may hinder communication or data transmission reliability.
- Data Security: Sensitive data traverses public networks, making robust encryption, multi-factor authentication, and ongoing cybersecurity vigilance absolute necessities to guard against breaches and unauthorized access.
Ongoing investment in secure network protocols is essential to maintain robust protection as threats evolve and technology standards change. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides in-depth guidance and standards for secure wireless communications.
Future Trends In Cellular Monitoring
The future of cellular monitoring is defined by enhancements in connectivity, intelligence, and automation. Upcoming trends include tighter integration with the Internet of Things (IoT), which will streamline data aggregation from hundreds or thousands of connected devices. The ongoing rollout of 5G technology is set to deliver lower latency and higher bandwidth, enabling faster response times and improved video and data quality compared to older standards.
Additionally, artificial intelligence is being integrated for advanced anomaly and threat detection as well as predictive analytics. These improvements will not only help organizations respond faster but also provide the insights needed to prevent problems before they escalate, ensuring smarter use of monitoring data across all sectors.
Conclusion
Cellular monitoring systems have established themselves as indispensable tools for organizations that prioritize agility, comprehensive coverage, and operational intelligence. By leveraging the strengths of mobile networks, these solutions enable real-time data collection, risk mitigation, and operational scalability like never before. As technology advances and emerging trends redefine what is possible, cellular monitoring will continue to play a vital role in the connected landscapes of security, healthcare, industry, and the environment.







No Comments